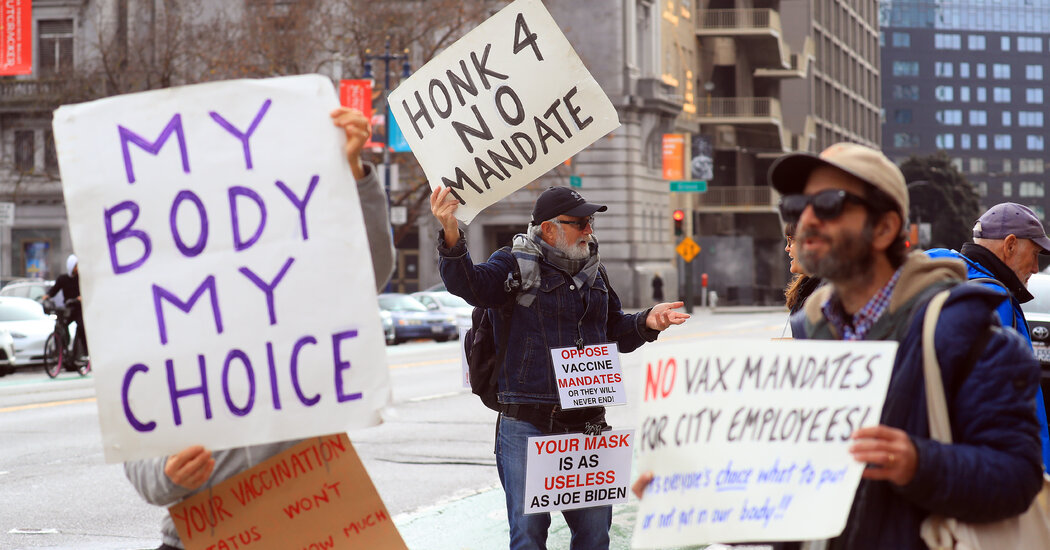
The Supreme Court is hearing arguments on Friday on the legality of two initiatives at the heart of the Biden administration’s efforts to address the coronavirus in the workplace through vaccine mandates.
The challengers — states led by Republican officials, businesses, religious groups and others — say Congress has not authorized the measures, adding that they are unnecessary and in some ways counterproductive.
The administration says that workplace safety and health care laws have given it ample authority to take bold action in the face of a lethal pandemic.
The more sweeping of the two measures, directed at businesses with 100 or more employees, would impose a vaccine-or-testing mandate on more than 84 million workers. The administration estimated that the rule would cause 22 million people to get vaccinated and prevent 250,000 hospitalizations.
The other measure requires workers at hospitals and other health care facilities that participate in the Medicare and Medicaid programs to be vaccinated against the coronavirus. The requirement would affect more than 17 million workers, the administration said, and would “save hundreds or even thousands of lives each month.”
The Supreme Court remains closed to the public, but the justices are taking the bench to hear the arguments in person and the court will provide a live audio feed on its website.
All of the justices are fully vaccinated and have received a booster shot, a court spokeswoman said.
The Supreme Court has repeatedly upheld state vaccine mandates in a variety of settings against constitutional challenges. The cases before the court are different, as they primarily present the question of whether Congress has authorized the executive branch to institute the requirements.
The answer will mostly turn on the language of the relevant statutes and on whether the administration followed proper procedures in issuing the requirements.
The vaccination-or-testing requirement for large employers was issued in November by the Labor Department’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA.
Employers are allowed to give their workers the option to be tested weekly instead of getting the vaccine, though they are not required to pay for the testing. The rule makes an exception for employees with religious objections and those who do not come into close contact with other people at their jobs, like those who work at home or exclusively outdoors.
Under a 1970 law, OSHA has the authority to issue emergency rules for workplace safety, provided it can show that workers are exposed to a grave danger and that the rule is necessary.
Jan. 7, 2022, 7:51 a.m. ET
States, businesses and others challenged the measure in appeals courts around the nation, and a unanimous three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit, in New Orleans, ruled in favor of some of the challengers, blocking the measure.
After the challenges were consolidated before the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit, in Cincinnati, a divided three-judge panel reinstated the measure.
“The record establishes that Covid-19 has continued to spread, mutate, kill and block the safe return of American workers to their jobs,” Judge Jane B. Stranch wrote for the majority. “To protect workers, OSHA can and must be able to respond to dangers as they evolve.”
In dissent, Judge Joan L. Larsen wrote that the administration “likely lacks congressional authority” to impose the vaccine-or-testing requirement.
“The mandate is aimed directly at protecting the unvaccinated from their own choices,” she wrote. “Vaccines are freely available, and unvaccinated people may choose to protect themselves at any time.”
The Coronavirus Pandemic: Key Things to Know
In the Supreme Court case, National Federation of Independent Business v. Department of Labor, No. 21A244, the challengers argued that the regulation did not address a workplace issue and so exceeded the agency’s lawful authority. “Covid-19 is not an occupational danger that OSHA may regulate,” lawyers for Ohio and 26 other states told the justices in a recent brief.
They added that agencies seeking to issue regulations on “major questions” with broad economic or political implications must have clear congressional authorization.
The second case, Biden v. Missouri, No. 21A240, concerns a regulation issued in November requiring health care workers at facilities that receive federal money under the Medicare and Medicaid programs to be vaccinated against the coronavirus unless they qualify for a medical or religious exemption.
States led by Republican officials challenged the regulation, obtaining injunctions against it covering about half of the nation. Two federal appeals courts, in New Orleans and St. Louis, refused to stay those injunctions while appeals moved forward.
A third federal appeals court, in Atlanta, sided with the Biden administration. “Health care workers have long been required to obtain inoculations for infectious diseases, such as measles, rubella, mumps and others,” Judges Robin S. Rosenbaum and Jill A. Pryor wrote for a divided three-judge panel, “because required vaccination is a common-sense measure designed to prevent health care workers, whose job it is to improve patients’ health, from making them sicker.”
The Biden administration argued that a federal statute gave it broad authority to impose regulations concerning the health and safety of patients at facilities that receive federal money. The statute gives the secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services the general power to issue regulations to ensure the “efficient administration” of the Medicare and Medicaid programs, and parts of the statute concerning various kinds of facilities generally also authorize the secretary to impose requirement to protect the health and safety of patients.
“It is difficult to imagine a more paradigmatic health and safety condition than a requirement that workers at hospitals, nursing homes and other medical facilities take the step that most effectively prevents transmission of a deadly virus to vulnerable patients,” Solicitor General Elizabeth B. Prelogar wrote in a Supreme Court brief.
In response, lawyers for Missouri and other states wrote that the “sweeping and unprecedented vaccine mandate for health care workers threatens to create a crisis in health care facilities in rural America.”
“The mandate would force millions of workers to choose between losing their jobs or complying with an unlawful federal mandate,” they wrote. Had a judge not issued an injunction, they added, “last year’s health care heroes would have become this year’s unemployed.”